The 3-Minute Rule for 16 Memory-Boosting Tips from Brain Scientists - The Healthy
 Learning Retention: 8 Proven Methods & Strategies to Recall Knowledge
Learning Retention: 8 Proven Methods & Strategies to Recall KnowledgeThe Ultimate Guide To 5 Tips for Knowledge Retention in a Digital World - Training

views the sounds, images, physical feeling, or other sensory information included. Your memory of that occasion is formed by your visual system (observing extravagantly developed structures and lush landscaping, for example), your acoustic system(the ringing of the fruit machine), and perhaps odor(the distinctive aromas pumped into each gambling establishment ). Research suggests we remember things better and retain them longer when we associate suggesting to them utilizing
 12 Strategies for improving memory and retention of knowledge ideas - improve memory, strategies, knowledge
12 Strategies for improving memory and retention of knowledge ideas - improve memory, strategies, knowledge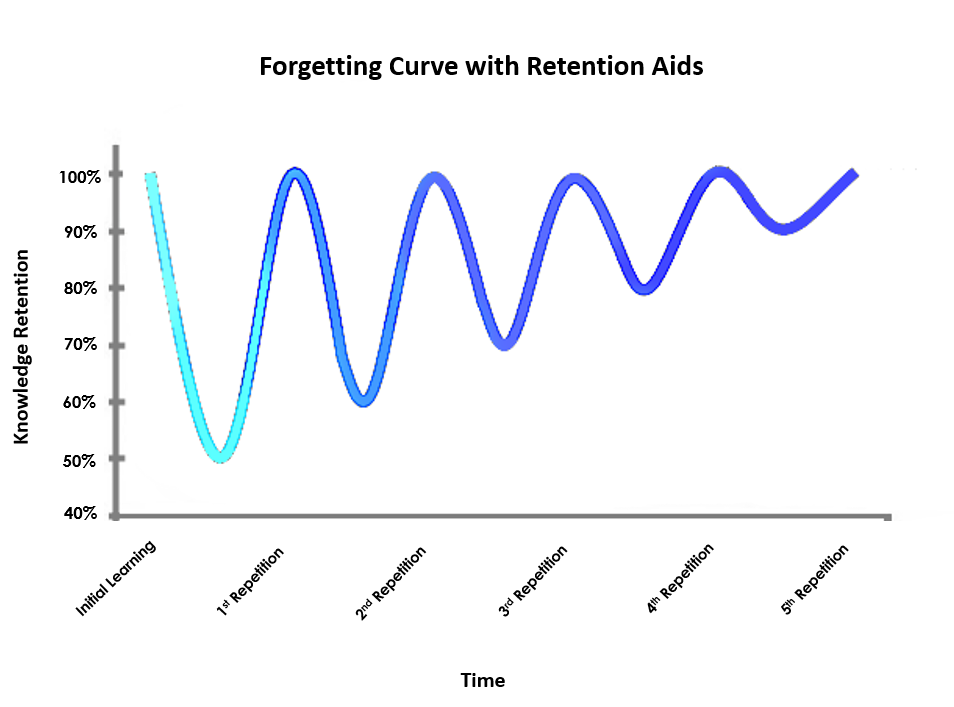 What every teacher should know about memory - Teacher Network - The Guardian
What every teacher should know about memory - Teacher Network - The Guardiansemantic encoding, If you attach indicating or factual understanding to any of this sensory input, that's called semantic encoding. This is good to know since research study suggests we remember things much better and retain them longer when we associate implying to them using semantic encoding. Find More Details On This Page , All of these bits and pieces of info are then stored in different areas of your brain. Your nerve cells (the afferent neuron in your brain )pass signals to each other about what you perceived, efficiently "talking"with each other and building either
short-term or long-lasting connections. The network of neurons in our brains are the key to storing and retrieving memories, There are 2 sort of memory: short-term and long-lasting. Short-term or working memory is like your brain's scratchpad. It's when your brain momentarily stores details prior to either dismissing it or transferring it to long-term memoryfor example, remembering what you wish to order for lunch prior to calling the takeout place. Long-term memories are those memories you hang on to for a couple of days or several years-- things like how to ride a bike or the very first dinner you had with the first individual you fell in love with. Both sort of memories can compromise with age because the brain loses cells vital to those connections in between nerve cells in time-- but that's not inevitable. Hence, remembering can be thought of as an act of imaginative reimagination. That's likewise why people can have
false-memory syndromes, or their memories of occasions may alter gradually. Now that we understand a few of how memory works, we can utilize that understanding to improve our memory. We'll start with the way of life modifications we can make, given that they can improve more than just our memory, and after that discuss particular memorization methods. These three things will offer you the.
