The Loss of Masculine With Declined Serum DHT Is - Frontiers Things To Know Before You Get This
 Dihydrotestosterone - Wikipedia
Dihydrotestosterone - Wikipedia How Can We Cure DHT Hair Loss? - ClinicExpert International Hair Transplant & Plastic Surgery
How Can We Cure DHT Hair Loss? - ClinicExpert International Hair Transplant & Plastic SurgeryExcitement About bep_0005.rst_post - BitTorrent.org
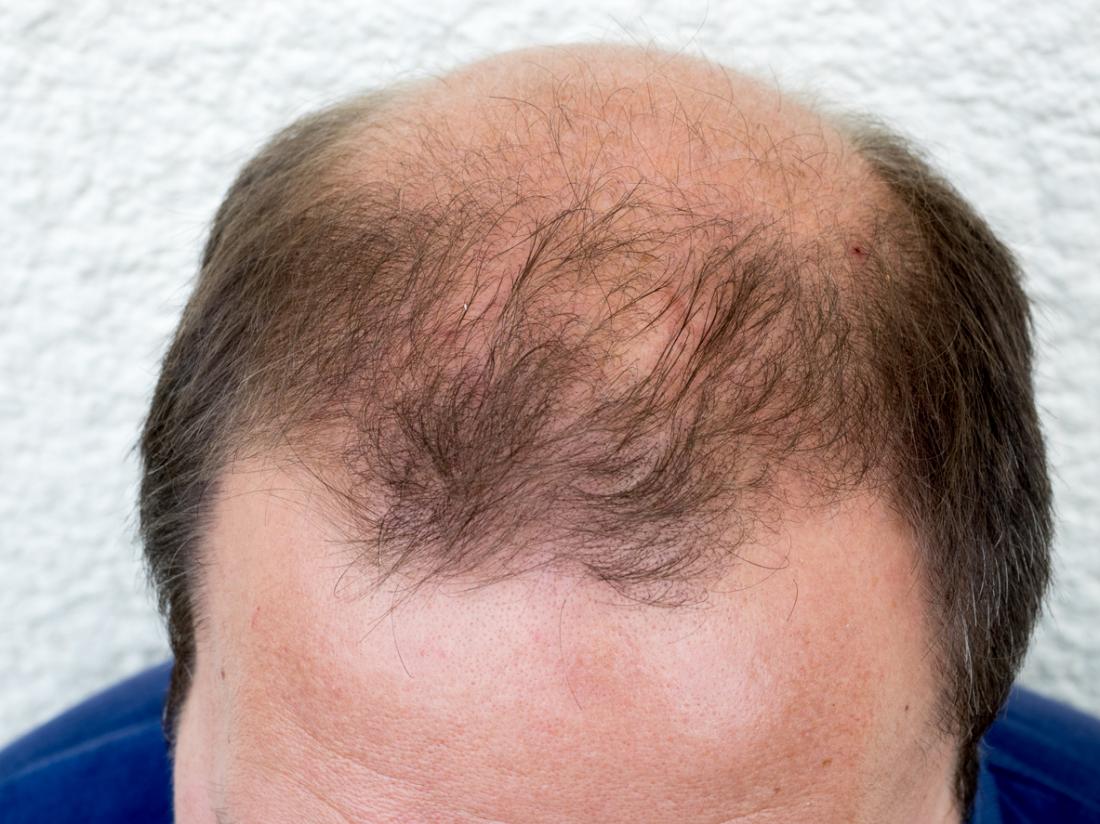
Male pattern baldness, or androgenetic alopecia, is the most typical type of loss of hair amongst males. Hormonal aspects appear to contribute, and specifically a male sex hormonal agent called dihydrotestosterone (DHT).Hair loss impacts around half of all guys over the age of 50 years, and around 50 million guys in the United States (U.S.).
Male pattern baldness impacts around half of men aged over 50 years in the U.S.DHT has many functions. Apart from hair production, it is connected to benign prostatic hyperplasia, or enlarged prostate, and prostate cancer too. DHT is a sex steroid, implying it is produced in the gonads. It is likewise an androgen hormone.
Throughout fetal advancement, DHT plays a vital role in the advancement of the penis and prostate gland. In males, the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase (5-AR) converts testosterone into DHT in the testes and the prostate. Approximately 10 percent of testosterone is normally converted into DHT.DHT is more effective than testosterone. It connects to the very same websites as testosterone, but more easily.
Indicators on DHT Holdings IncStock Quote (US: NYSE) - MarketWatch You Should Know
Male pattern hair loss is the most typical kind of loss of hair in males. Hair at the temples and on the crown slowly thin and eventually disappear. The precise factor why this occurs is unknown, however hereditary, hormonal, and environmental aspects are all believed to contribute. DHT is thought to be a major factor.

 THE TRUTH BEHIND DHT BLOCKERS- PROS & CONS! - AHS India
THE TRUTH BEHIND DHT BLOCKERS- PROS & CONS! - AHS IndiaHair growth is split into three phases: anagen, catagen, and telogen: is the growth phase. Hairs remain in this stage for 2 to 6 years. The longer it lasts, the longer the hair grows. Usually, around 80 to 85 percent percent of the hairs on the head remain in this phase.
It permits the hair follicle to restore itself. is the resting phase. The hair follicle lies inactive for 1 to 4 months. Normally in between Rogaine and 20 percent of hairs remain in this stage. After this, anagen begins again. The existing hair is pressed out of the pore by the new development and naturally sheds.
